by Michael Prodinger, Rita Stampfl and Marie Deissl-O'Meara (University of Applied Sciences Burgenland)
The following article deals with the implementation of a Learning Assistant, an advanced tool based on artificial intelligence (AI) that provides continuous learning support to students. The assistant is used in distance learning programmes at FH Burgenland Continuing Education. With ChatGPT installed and integrated into the Learning Management System (LMS), it functions as an assistant with the ability to answer questions from students whenever they arise. Additionally, a course teacher verifies and corrects the AI’s responses within 24 hours to guarantee the system’s correctness and dependability.
The ongoing digitalisation and transformation of higher education (HE) creates new opportunities for innovative teaching methods, especially in the area of distance learning. Teachers should thus concentrate on how digital tools are transforming education. It is therefore crucial that they develop strategies to offer attractive digital education options to learners [1]. The proposed addition of a Learning Assistant to the FH Burgenland Continuing Education distance learning programmes [L1] is one specific illustration of this development. A closer examination of the several facets of this innovation, how it works, and the associated added value for students, is conducted in light of its successful implementation at other institutions [L2].
The Learning Assistant is designed as an AI tool that provides interactive learning support to students at any time of the day or night. Its main function is to answer students’ content-related questions, using only the content stored in the LMS. This specific configuration ensures that the information and answers provided are always relevant to the programme and aligned with the curriculum. The integration of the Learning Assistant into the LMS therefore represents a targeted extension of the existing resources, with the aim of providing students with an additional information channel for acquiring knowledge and clarifying any uncertainties. It is clear that learning assistants will permanently change the way we teach and learn [L3].
At the heart of the Learning Assistant is an AI system based on the Large Language Model (LMM). This is an advanced technology capable of generating and understanding human-like text [L4]. LLMs have gained prominence in HE, especially with the integration of ChatGPT, which uses AI to interact with users. If used responsibly by all stakeholders, LLMs can improve the quality of distance learning assignments [2]. In the context of distance learning, the LLM is configured to use the content stored in the LMS as the basis for its responses.
A key benefit of the Learning Assistant is its availability. Students may engage in conversation with the AI and pose questions whenever necessary. This is especially crucial for FH Burgenland distance learning students because they frequently have jobs and require flexible access to learning resources and support. A continuous and self-directed learning process is made possible by the Learning Assistant’s availability for communication at all times. The use of digital educational tools can encourage extensive participation as they are widely available, tailored to the specific needs and prior knowledge of the learner, thus enabling targeted learning [L5]. The key challenge is to ensure that AI applications are used effectively in education, while proactively addressing the inherent risks [L6].
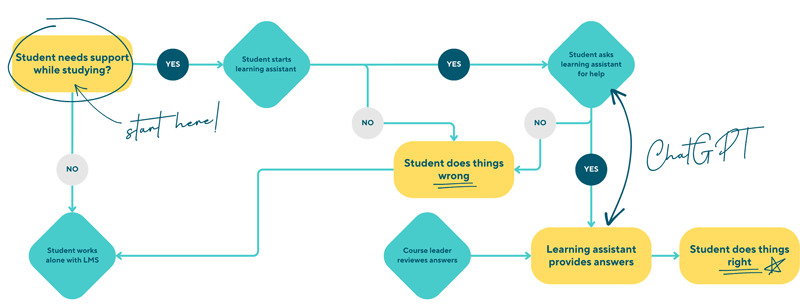
Figure 1: Support process with Learning Assistant.
ChatGPT is a powerful AI technology that powers the Learning Assistant and allows for communication between students and the assistant. Chat GPT has the ability to understand and respond to natural language, ensuring intuitive and user-friendly communication. With ChatGPT's natural language understanding and response capabilities, communication is clear and easy to use. The Learning Assistant is ChatGPT. It is integrated into the existing LMS, contributing to a smooth and effective learning experience.
A systematic review process is in place to ensure the reliability and accuracy of the information provided by the Learning Assistant. Within 24 hours of the interaction with the Learning Assistant, course leaders review the results and make corrections to the answers where necessary. This is to identify and correct any possible errors or misunderstandings caused by ChatGPT [L2]. Course tutors therefore play a crucial role in ensuring the quality and accuracy of the support provided by the Learning Assistant.
The introduction of a new system to reduce the workload of programme directors is a strategic step that promises to significantly reduce administrative and organisational workloads. It is expected that this reduction in workload will lead to strong support for programme directors as they will benefit directly from the increased efficiency. Course directors will therefore not only support but also actively promote the introduction of Learning Assistants, as they will play a key role in optimising and improving course.
In conclusion, the Learning Assistant is an innovative and valuable addition to distant learning courses. The combination of advanced AI technology, continuous availability and systematic progress monitoring creates a comprehensive and flexible learning experience that helps students to reach their full potential. The article underlines the importance of this innovation for HE and highlights the many opportunities that the use of AI in education opens up by creating flexible, personalised and efficient learning environments [2].
Links:
[L1] https://fh-burgenland-weiterbildung.at/en/
[L2] https://www.iu.de/news/syntea-ki-gestuetzte-loesung-revolutioniert-online-bildung-und-interaktion-mit-studierenden/
[L3] https://www.faz.net/aktuell/karriere-hochschule/ki-in-der-schule-enkelejda-kasneci-ueber-potential-und-risiken-18911332.html
[L4] https://www.itportal24.de/ratgeber/large-language-models
[L5] https://www.bmbwf.gv.at/Themen/HS-Uni/Hochschulgovernance/Leitthemen/Digitalisierung/K%C3%BCnstliche-Intelligenz.html
[L6] https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/library/factsheet-artificial-intelligence-europe
References:
[1] N. Iivari, S. Sharma, and L. Ventä-Olkkonen, “Digital transformation of everyday life – How COVID-19 pandemic transformed the basic education of the young generation and why information management research should care?,” Int. J. of Information Management, vol. 55, 102183, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2020.102183
[2] T. Schmohl, A. Watanabe, and K. Schelling (Editors), “Artificial Intelligence in Higher Education. Opportunities and limits of AI-supported learning and teaching [Künstliche Intelligenz in der Hochschulbildung. Chancen und Grenzen des KI-gestützten Lernens und Lehrens],” 2023. https://doi.org/10.25656/01:26427
Please contact:
Michael Prodinger, University of Applied Sciences Burgenland, Austria











