by George Hatzivasilis and Sotirios Ioannidis (Technical University of Crete)
Open source solutions empower innovation and accessibility worldwide, but their security challenges can hinder responsible and inclusive digital development. The EU-funded SecOPERA project addresses this by delivering a holistic framework for securing open source software and hardware, reinforcing trust and sustainability.
Open source software (OSS) and open source hardware (OSH) have transformed digital ecosystems, democratising technology and fostering inclusive innovation. However, their security gaps remain a barrier to sustainable adoption. While open source solutions and free versions provide great flexibility and transparency, they often lack the dedicated security assurance and professional support that commercial products typically receive. Many open source components are maintained by small communities or volunteers without formal security audits, making them vulnerable to unnoticed flaws and slow patching cycles. This gap can deter organisations and public services from adopting open solutions, even when they would otherwise benefit from their adaptability and cost-effectiveness.
The EU Horizon Europe project SecOPERA (Security Assurance and Hardening for Open Source Software and Hardware) [L1] responds to this challenge by providing a comprehensive security framework tailored for the complexities of open solutions. The approach aligns with the goals of responsible innovation and inclusive digital infrastructures, ensuring that openness does not come at the cost of trust.
A key concept in SecOPERA is the decomposition of any open source solution into four interrelated layers [1]:
- Device Layer: Open hardware cores and processors.
- Application Layer: Libraries, OS kernels, and software frameworks.
- Network Layer: Open network stacks and security libraries.
- Cognitive Layer: Machine learning models and training datasets.
Each layer faces distinct threats, requiring specialised security checks and mitigations. SecOPERA introduces Secure Flows, an end-to-end proof that open source components work together securely without creating hidden vulnerabilities [1]. This layered auditing ensures that even highly interconnected OSS/OSH systems can be trusted in critical contexts.
SecOPERA’s methodology rests on five pillars: Decompose, Audit/Assess, Secure, Adapt, and Update/Patch (see Figure 1). Decomposition maps out all components and dependencies, building clear security boundaries. The Audit/Assess pillar applies state-of-the-art techniques, including static and dynamic analysis, fuzzing, and cross-layer penetration testing. The Secure pillar provides add-on security modules, such as trusted computing extensions or quantum-safe cryptography. Adapt focuses on code debloating to reduce attack surfaces, while Update/Patch automates ongoing monitoring and patching, ensuring long-term resilience.
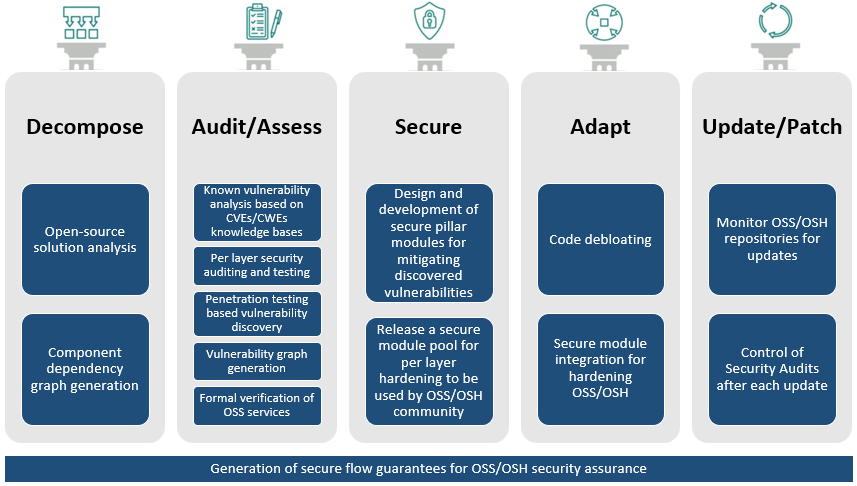
Figure 1: The SecOPERA functionalities.
By embedding security assurance throughout the open source lifecycle, SecOPERA empowers developers and maintainers to adopt DevSecOps practices without sacrificing openness. This supports more inclusive technology by making robust security accessible even for communities or SMEs lacking dedicated security teams.
To validate its impact, SecOPERA deploys its framework in real pilots (see Figure 2). In the automotive supply chain, PINNO and VoXel use SecOPERA’s tools to secure co-developed hardware/software prototypes and maintain ISO-compliant DevSecOps practices. In smart city water management, GreenCitizen applies SecOPERA to secure IoT devices monitoring urban water infrastructure, ensuring safe and sustainable services for communities [1].
According to the Open Source Security and Risk Analysis (OSSRA) Report [2], a typical application today includes hundreds of open source components maintained by diverse communities. Keeping such ecosystems secure requires collaborative, transparent, and automated assurance. SecOPERA addresses this challenge with a unified hub architecture, combining a dashboard, orchestrator, audit engines, secure module pools and update mechanisms. This creates a European-scale playground for collaboration, where open source modules can be securely analysed, hardened and shared [1].

Figure 2: SecOPERA use cases of automotive supply chain and smart city water management.
By strengthening security without undermining openness, SecOPERA demonstrates that responsible innovation and inclusion can go hand in hand. Trustworthy open source infrastructures empower diverse user communities, reduce digital divides and foster sustainable growth.
As digital technologies advance, securing openness becomes a societal imperative. SecOPERA shows how Europe can lead by example, turning security into an enabler for accessible, professionally trusted, and resilient digital futures.
Link:
[L1] https://secopera.eu/
References:
[1] A. Fournaris et al., Providing Security Assurance & Hardening for Open Source Software/Hardware: The SecOPERA approach, IEEE CAMAD 2023.
[2] Synopsys Inc., Open Source Security and Risk Analysis (OSSRA) Report 2025.
Please contact:
George Hatzivasilis
Technical University of Crete (TUC), Greece










