by George Tzagkarakis (FORTH-ICS), Rommert Dekker (EUR-DE), and Themis Palpanas (UPC- LIPADE)
Effective decision-making in large-scale, uncertain systems faces growing challenges in today’s complex, data-rich environments. Traditional systems struggle to process vast datasets in real time while balancing conflicting objectives and ensuring fairness. The TwinODIS project introduces a transformative approach by combining Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Operations Research (OR) to create next-generation Decision Intelligence systems. This integration leverages advanced analytics, optimisation techniques, and AI-driven insights to transform large-scale decision-making, enabling sustainable development and economic growth through smarter, data-driven solutions.
Traditional decision support systems struggle to meet the demands of today’s data-intensive and uncertain environments. While data provides valuable insights, the real challenge lies in transforming it into timely, impactful decisions. Existing systems often lack the agility and intelligence required to process vast, complex datasets and respond to dynamic conditions. As the need for autonomous, AI-driven decision-making grows, the European Union is investing heavily in AI and the data economy, with spending expected to surpass €70 billion by 2026. Regulatory frameworks like the AI Act [1] and Data Act [2] aim to establish Europe as a global leader in data-driven decision-making, fostering sustainable development and economic progress. The EU’s “2030 Digital Compass” envisions resilient, agile societies built on intelligent systems that convert knowledge into action, driving innovation and workforce transformation.
The TwinODIS project [L1], funded by the EU under Horizon Europe HORIZON-WIDERA-2023-ACCESS-02-01 Twinning Programme, introduces advanced technologies to transform large-scale decision support systems in dynamic, data-rich environments. To address the challenge of managing complex big data, it will develop distributed storage systems and real-time predictive and prescriptive analytics to process vast volumes of data efficiently. For adaptive decision-making, TwinODIS combines AI techniques such as Reinforcement Learning with Operations Research methods like uncertainty-aware optimisation to ensure responsiveness in uncertain systems. It also tackles the complexity of conflicting objectives by using AI-driven multi-level optimization and metaheuristics, such as swarm intelligence, to solve high-dimensional problems while minimising computational demands. To promote fairness and transparency, the project incorporates bias-reducing data re-weighting methods and explainability tools, enabling human-understandable and unbiased decision-making. These innovations mark a significant advancement in scalable, intelligent, and equitable decision systems.
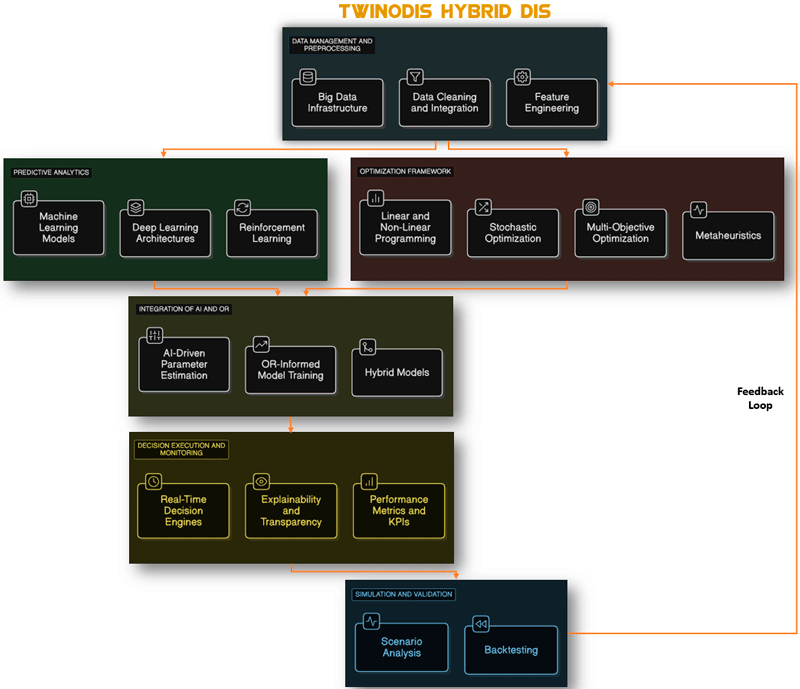
Figure 1: Architecture of TwinODIS decision intelligence system.
The transition to AI-driven decision-making in data-intensive and uncertain environments relies on a multidisciplinary approach that integrates Computer Science and Operations Research (see Figure 1). This is the focus of TwinODIS, which unites the Institute of Computer Science (ICS) at the Foundation for Research and Technology - Hellas (FORTH) with two renowned European institutions, namely, Université Paris Cité (UPC) - Laboratory of Informatics Paris Descartes (LIPADE) and Erasmus University Rotterdam (EUR) - Department of Econometrics (DE).
Real-time OR techniques are indispensable for decision-making in today’s fast-paced and dynamic environments. Unlike traditional OR, which relies on historical data and fixed models, real-time OR utilises live data streams for swift responses to changing conditions, particularly crucial in sectors like energy, transportation, and emergency response. FORTH-ICS excels in computational methods for time series data in IoT and remote sensing applications. With EUR-DE’s expertise in online optimisation, stochastic dynamic programming, risk and uncertainty management, and large-scale multi-objective problem-solving, this collaboration will yield innovative data-driven optimisation and adaptive decision-making, ensuring agility in uncertain data and model situations. Furthermore, the convergence of AI and OR creates powerful systems that enhance decision support capabilities in complex, data-rich environments. In TwinODIS, UPC-LIPADE’s expertise in big data and distributed/explainable AI combines with EUR-DE’s strengths in multi-objective optimisation and metaheuristic algorithms, to advance FORTH-ICS’s machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) deployment capabilities. This collaboration integrates AI and OR by improving ML/DL training with advanced optimisation, using ML/DL models to inform OR methods like linear programming, and leveraging ML/DL for pattern recognition, reinforcement learning, and uncertainty handling in large-scale decision-making frameworks.
The TwinODIS project targets two critical applications: multi-energy systems management and smart ports planning, both of strategic importance to the EU. In multi-energy management, TwinODIS addresses the challenge of coordinating renewable and non-renewable energy sources, aiming to enhance energy autonomy and efficiency. The system uses real-time data and hybrid AI-OR models to optimise energy demand, supply forecasting, and grid stability, with key performance goals such as reducing energy costs and increasing renewable energy usage. In smart ports planning, TwinODIS will implement hybrid deep reinforcement learning models to optimise vessel scheduling, berth allocation, and resource distribution at ports. The system will leverage real-time data to improve port efficiency, reduce turnaround times, and decrease CO2 emissions. Both applications will be evaluated through backtesting and simulations using real-world data from partners like the Dutch Energy Dashboard and the Port of Rotterdam Authority.
Link:
[L1] https://spl.ics.forth.gr/twinodis
References:
[1] Artificial Intelligence Act, European Parliament, Legislative Observatory (OEIL). [URL: https://kwz.me/hFY]
[2] Data Act, European Parliament, Legislative Observatory (OEIL). [URL: https://kwz.me/hFB]
Please contact:
George Tzagkarakis, FORTH-ICS, Greece
Rommert Dekker
Erasmus University Rotterdam, The Netherlands
Themis Palpanas, Université Paris Cité, France











