Chatzigiannakis Ioannis (Sapienza University of Rome and CNIT), Giordano Silvia (University of Applied Science of Southern Switzerland - SUPSI), Orphanoudakis Theofanis (Hellenic Open University)
Extended Reality (XR) has become a tangible possibility to revolutionise educational and training scenarios by offering immersive, interactive and personalised experiences. The XR2Learn [L1] project aims to establish a cross-border innovation community for XR in learning, bringing XR technology providers, application designers, education experts, application developers, end-users and decision-makers in direct access to communicate, collaborate and matchmake interests enabling also bottom-up innovation creation.
The proliferation of personal and mobile devices equipped with enhanced processing and networking capabilities has facilitated the realisation of XR across diverse innovative domains. XR is no longer confined to research labs or exclusive to corporate entities, nor does it necessitate substantial investments in specialised software, hardware, or expert teams. Instead, it can be approached as a viable endeavour accessible to a broader audience.
While XR technology holds promise for diverse applications across various sectors, its primary utilisation currently revolves around gaming, entertainment, engineering, and medicine, with tourism and e-commerce following suit. Surprisingly, the educational realm lags significantly behind, despite abundant literature showcasing XR's myriad benefits in this domain: expanding knowledge domains, fostering active learning experiences, enhancing comprehension of complex subjects, mitigating distractions during study sessions, stimulating creativity among students, and enhancing learning efficiency, among others. The increasing demand for lifelong learning and the necessity to upskill/reskill individuals from diverse backgrounds, with varying levels of IT literacy and linguistic diversity, mandates the integration of XR technologies into educational and training frameworks. For instance, the manufacturing industry grapples with the substantial challenge of training its workforce on emerging Industry 4.0 and 5.0 technologies on a global scale.
The XR2Learn project has developed an innovation platform that promotes cross-discipline fertilisation with the aim of reducing the costs of developing XR applications tailored for the education domain (see Figure 1).
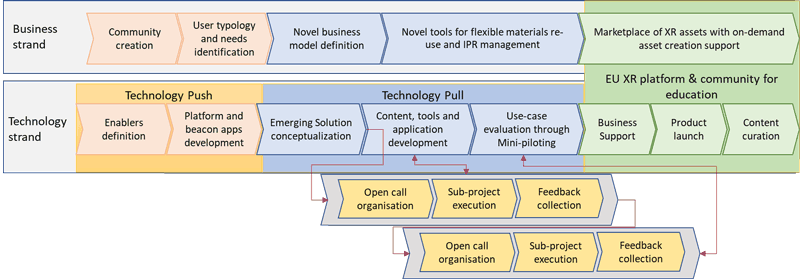
Figure 1: Structure of the XR2Learn project innovation platform.
At the technical level, the platform incorporates a range of solutions made available for free to the EdTech community ranging from ready-to-explore and experiment-with-beacon applications, to AI-assisted software enablers and \models and low-code tools to reduce the development life-cycle of Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITS) that enable the adaptation of interactive and virtual experience-based learning activities. The INTERACT tool included in the XR2Learn platform goes beyond basic 3D object manipulation and avatar navigation in virtual environments by addressing aspects such as ergonomics, advanced physics for object and trajectory tracking, and more [1]. The Lego-like approach democratises the virtual simulation, easing to everybody the development of XR applications. A toolchain of innovative components is also included for emotion/affect detection and for automated adaptation of the learning experience to the user needs and emotions, supporting the delivery of applications enriched by affective computing [2]. In doing so, XR2Learn promotes personalised immersive learning experiences that increase the educational solution effectiveness.
At a business level, the platform supports the commercialisation of innovative competitive use-case driven applications by assisting innovators in liaising and collaborating with education experts, which can assist in sound educational scenario definition to ensure market potential. Special emphasis is given to the validation of applications by organising pilots and setting-up campaigns with early adopters, involving trainers and training institutions to cooperate with and deliver sound assessments [3]. A tool for flexible IPR management and licensing through NFTs is included to promote easy trading of all types of resources including 3D models, scenes, software modules applications and tools and support innovators and even individual professionals create and share resources, fuelling new business models and the creation of new roles.
The XR2Learn platform extends beyond a catalogue facilitating easy access to solutions and becomes itself a tool towards efficient user/provider on-demand collaboration boosting innovation. XR2Learn focuses on the development of a functional ecosystem with active stakeholder engagement, training and support leveraging innovative business models towards its sustainable future evolution. With the support of the Horizon Europe programme, XR2Learn is organising two open calls to further support digital start-ups, SMEs and industry active in the sector through Financial Support for Third Parties actions allowing them to further advance early prototypes of XR educational solution to a market-ready product, with the overall aim to populate the on-demand education platform.
During 2023 XR2Learn carried out the first open call, providing support for fully developed, tested and ready-to-deploy digital learning solutions/apps using XR technologies. Seven projects have been selected that will go through a fast-paced acceleration programme with focus on the development of content, tools and applications that will be ready for validation [L2].
During 2024 a second open call will be performed aiming to support innovative SMEs in piloting XR-based applications in relevant environments to reach high Technology Readiness Levels (TRL) and Market Readiness Levels (MRL).
Links:
[L1] https://xr2learn.eu
[L2] https://xr2learn.eu/open-call-1/
References:
[1] R. K. G. R. Thandapani, B. Capel, A. Lasnier, and I. Chatzigiannakis, “INTERACT: An authoring tool that facilitates the creation of human centric interaction with 3d objects in virtual reality,” in Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Mobile Human-Computer Interaction, pp. 1–5. 2023.
[2] S. M. H. Mousavi, M. Besenzoni, D. Andreoletti, A. Peternier, and S. Giordano, “The Magic XRoom: a fexible VR platform for controlled emotion elicitation and recognition,” in Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Mobile Human-Computer Interaction, pp. 1–5, 2023.
[3] K. Theodora, A. Fanariotis, V. Fotopoulos, C. Karachristos, and T. Orphanoudakis, “Why re-focus on IoT in education? Evidence of the PARADIGM project,” in 2023 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE), pp. 01–09, IEEE, 2023.
Please contact:
Ioannis Chatzigiannakis, Sapienza University of Rome and CNIT, Italy











