by Kübra Yayan (Eskisehir Osmangazi University), Yunus Emre Esen (LTG), Uğur Yayan (Eskisehir Osmangazi University)
Embarking on an innovative journey, the XR4HRC (Excellence in Extended Reality for Human-Robot Collaboration) project within the XR2Learn initiative redefines vocational training in the robotics sector through Extended Reality (XR) technologies. This endeavour aims to elevate workforce competencies, quality assurance, and human-robot synergy to new heights, perfectly aligning with the progressive vision of Industry 5.0.
The XR4HRC project (see concept sketch in Figure 1), part of the XR2Learn initiative, which started on 01.01.2024, seeks to transform vocational training and quality control in the robotics and automation sectors using XR. It aims to improve training effectiveness, minimise cognitive load, and increase workforce efficiency, in line with Industry 5.0's requirements. The project highlights advanced human-machine collaboration through immersive learning experiences.

Figure 1: XR4HRC concept sketch.
Key to XR4HRC is the A New Dimension of Learning: Exploring the Impact of XR4HRC on Training Efficacypartnership among LTG (a technology development and R&D oriented SME in Turkey), known for AR/VR/XR expertise, IFARLAB-DIH at Eskisehir Osmangazi University (Turkey) with its focus on robotics digital competencies, and BEST (Austria), a leading VET provider in Vienna. These collaborations are essential for embedding XR in vocational training to meet the demands of modern industries.
The initiative represents a significant leap in vocational education, using XR to equip the workforce with critical skills, improve quality control, and promote effective human-robot interactions. It emphasises the role of XR in cutting development costs and enhancing knowledge sharing, aiming to strengthen European XR market competitiveness, especially for SMEs, by offering inclusive and innovative training solutions.
Training Scenarios
The XR4HRC project has developed a comprehensive suite of training scenarios (Figure 2) utilising the immersive potential of XR to advance vocational training in the robotics sector. These scenarios are meticulously designed to not only acquaint trainees with their future work environment but also to ensure their mastery of essential maintenance and safety protocols, critical for secure and efficient operations.
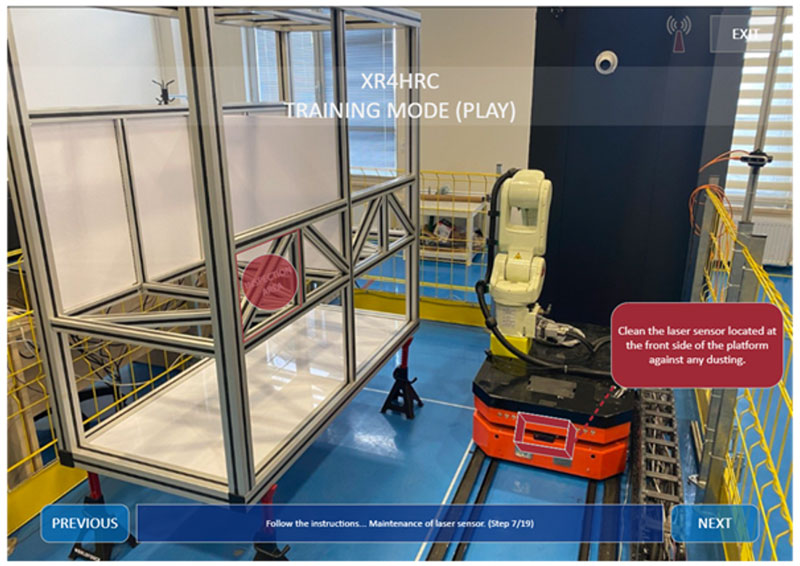

Figure 2: Training mode.
Training Scenarios Overview
Introduction to the Laboratory Environment: This initial scenario introduces trainees to a simulated factory environment, providing a detailed orientation to the workspace, the robot arm, and the robot chassis cabinet, ensuring trainees are well-versed in the operational landscape.
General Maintenance of the Robot Arm: Focusing on the upkeep of the robot arm, this module equips trainees with the necessary knowledge and skills for routine maintenance, emphasising the practical aspects of robotics care to enhance machine longevity and reliability.
Safety Training for Working Safely with the Robot Arm: Dedicated to safety, this scenario integrates critical safety instructions into the XR training, covering essential precautions such as pedestrian-robot path separation, light curtains, and protection against unintended robot movements.
Remote Assessment Enhancement: The project innovates vocational training assessments by introducing remote VR exams, enabling a dynamic and interactive competency evaluation (Figure 3). This approach places both the trainee and evaluator within the same virtual environment, facilitating a real-time, in-depth assessment of the skills and procedures learned during training.
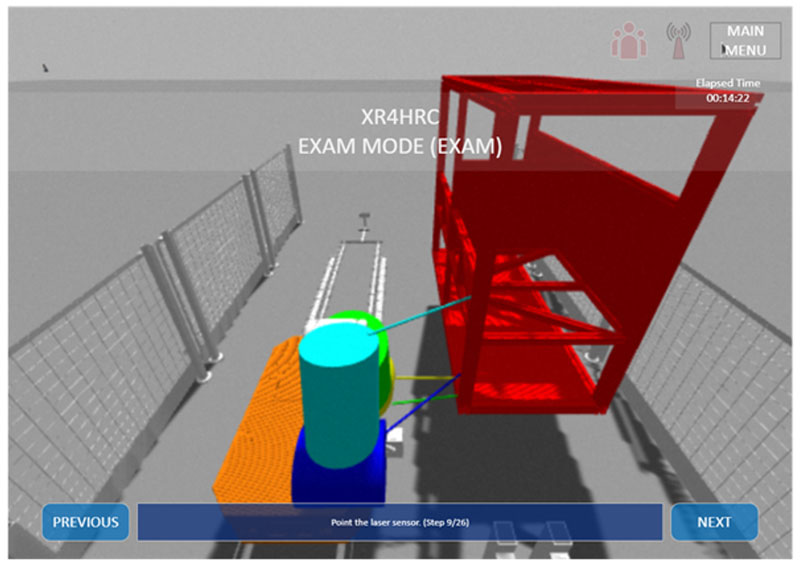
Figure 3: Exam mode.
Integrating remote VR exams into the XR4HRC initiative marks a significant leap in vocational training assessment methods, utilising VR technology to make evaluations more efficient, engaging, and safe.
Implementation of the XR System in the XR4HRC Project
Within the XR4HRC project, training sessions employ Augmented Reality (AR) to superimpose crucial information onto physical components in the laboratory, enhancing the learning experience. In contrast, assessments utilise Virtual Reality (VR) to fully immerse trainees in a virtual laboratory setting, allowing for an in-depth evaluation of their skills.
The project integrates the Meta Quest 3 hardware, chosen for its advanced passthrough technology, which merges real and virtual environments using the device's front-mounted camera and sensors [L1]. This fusion of realities is augmented by the ability to interact with virtual objects using the headset's controllers or direct hand movements.
Unity is the primary development platform for the XR4HRC modules, selected for its vast library of assets and the adaptability of C# scripting, crucial for customising virtual components to meet the project's educational goals. The “Interact” plugin within Unity is vital for crafting scenarios, especially for the assessment modules, offering features like kinematic movement simulation and 3D model integration [L2], thus ensuring the virtual laboratory's realism. Developed by the LS-Group in France, this plugin facilitates sophisticated development, making it approachable for users with limited programming expertise.
To prepare for multi-user assessment modules, the project addresses network challenges, particularly synchronisation and latency. The “Netcode” Unity plugin is employed to establish stable communication channels between participants and evaluators, using a server-client model to reduce network inconsistencies, ensuring a smooth and synchronised virtual experience [1], [2].
Discussion
The XR4HRC project, within the XR2Learn initiative, targets the modernisation of VET in alignment with Industry 5.0, utilising XR to enrich training in robotics. It emphasises practical skills, quality control, and human-robot collaboration. While showcasing the potential of XR to enhance learning and operational efficiency, the project also confronts challenges such as remote collaboration and the need for higher Technology Readiness Levels (TRLs) to ensure real-world applicability.
Conclusion
The XR4HRC project endeavours to enhance VET within the robotics sector through XR technologies, focusing on immersive and interactive training experiences. As the project progresses, it seeks to overcome existing challenges and achieve higher TRLs, laying the groundwork for future advancements in XR-based vocational training.
The XR4HRC Project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation action programme (grant agreement Nr. 101092851).
Links:
[L1] https://developer.oculus.com/documentation/unity/unity-passthrough/
[L2] https://www.ls-group.fr/interact
References:
[1] T. Uzlu and E. Şaykol, Evaluating a Player’s Network Class in a Multiplayer Game with Fuzzy Logic, Gümüşhane Üniversitesi Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü Dergisi.
[2] M. Ahmed, S. Reno, M. R. Rahman ve S. H. Rifat, “Analysis of Netcode, Latency, and Packet-loss in Online Multiplayer Games,” ICAISS.
Please contact:
Kübra Yayan, Eskisehir Osmangazi University- Intelligent Factory and Robotics Laboratory, Turkey
Yunus Emre Esen, LTG (Lider Teknoloji Gelistirme), Turkey











