by Paul Isaris (SciFY PNPC), George Giannakopoulos (SciFY PNPC), Alexandros Tzoumas (SciFY PNPC)
Health-related news articles have become increasingly significant during the past few years, especially in crisis times. Their impact can be significant, to communicate critical knowledge, but also to bend the truth and provoke unwanted reactions from the public, or even reduce the efficacy of large-scale health efforts. However, Artificial Intelligence can support the reader when evaluating news items related to health by summarising different views on the same subject into a single, non-redundant summary. Such tools can change the way we interact with health news sources, help us build trust, and empower our verification capacity.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) changes the way we work, get informed, and interact with our community. An increasing number of news websites now operate with the help of AI in order to offer rapid and evidence-based journalism.
However, in the era of real-time information and rapid news coverage, one needs to verify the integrity of the news they read, and more so when it concerns health news streams. AI can support the user in such tasks, related to the trustworthiness of an article. On the other hand, the fact that news agencies rely significantly on automation and AI in order to produce news articles has led to a situation where the quantity of news articles battles the quality of the information offered. In health-related news, this is of great importance, since readers may pick a free online article over an expensive and time-costly appointment with the doctor. Thus, in such cases, evidence and science-backed content are critical.
Ideally, a health news article should list its source scientific publications, or surveys, or be verified by a human with a specialty in the related health sector. “Fake news”, i.e. false, or misleading information presented as news, can often (mis)lead readers to believe something that has not been backed by evidence or that is damaging to another person or a cause. This is especially true for people with reduced digital literacy since they are not usually able to do their own research on what they read. Integrity and truth are of great importance, especially in an era when thousands of news articles are being published every hour, and the number of news sources is excessive.
In such a setting, we can use AI to identify, across many sources, clusters of news items about the same topic, and use automatic summarisation techniques to create summaries that offer all the viewpoints, without redundancy, keeping the links to the original sources. This keeps the human in the communication loop, allowing them to correct and filter out any misleading information, while using computers to speed up the collection of news items, searching for similar texts, and providing a holistic view for the human to evaluate.
NewSum is a news summarisation app for Android devices [F1]. It is the first application to automatically create news summaries from multiple sources, based on multilingual summarisation research [1,2]. Offered in Greek and English, the app [L1] outlines the main points provided by the different news sources, without redundancy, facilitating the reader. Another demonstration of NewSum relates to the Social Web Observatory Project [L2], which overviews the trends of news sites and social media.
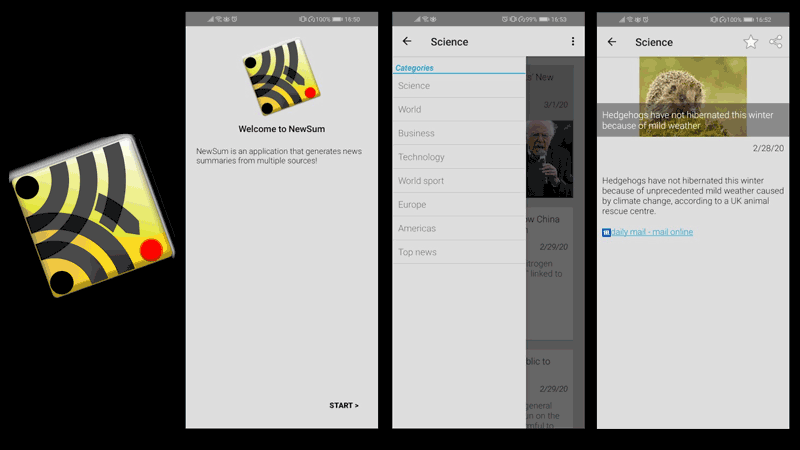
Figure 1: Newsum offers a wide variety of news articles, automatically summarised into cohesive texts.
Thousands of users have used it on a daily basis for real-time, multilateral news reading. By using a simple yet intuitive user interface, NewSum is applicable also to users with little-to-no familiarity with technology. This allows NewSum to act not only as a useful news summarisation mobile app, but also as an entry-level technological path for people with little-to-no experience with mobile apps and technology.
SHAPES (Smart and Health Ageing through People Engaging in Supportive Systems) [3] is an Innovation Action funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 programme involving 36 partners from a total of 14 European countries. It aims at creating an integrated IT platform that will bring together a wide range of digital solutions focused on improving the health, wellbeing, and independence of people as they get older. Sustaining longer and healthy lives requires solutions that minimise risks of injury, frailty, and long-term chronic diseases. These solutions also relate to how the ageing population will adapt to the information flux from online sources. This is where NewSum comes in.
NewSum participates as a Digital Solution in the “LLM CARE Healthcare System for Cognitive and Physical training / Improving In-Home and Community-based Care” Pilot, which will run in three countries. This pilot includes, among other outcomes, several non-pharmaceutical interventions against cognitive deterioration, but also an increased connection of the elderly to the wider community and environment. The contribution of NewSum relates to facilitating health news reading and connecting the elderly to the wider world, through news. It is also expected to help the reader retain critical evaluation capacity and access trustworthy health news. To this end, NewSum emphasizes multi-lateral viewpoints. It also provides links back to the sources allowing validation of the claims and enables holistic updates, reducing the effect of “information bubbles” that strongly bias the reader. The above points, coupled with appropriate inclusive user interfaces, remove technology skill and age barriers and support trust-building and equal information access across societal and age strata. This, in turn, builds a common ground for discussion with peers, allows information processing and related high cognitive functions to be retained through daily interaction, and forms a non-intrusive (information) accessibility solution.
Links:
[L1] https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=gr.scify.newsum.ui&hl=el&gl=US
[L2] https://socialwebobservatory.iit.demokritos.gr/#/about
References:
[1] G. Giannakopoulos, G. Kiomourtzis, V. Karkaletsis: “NewSum: ‘N-Gram Graph’-Based Summarization in the Real World”, in Innovative Document Summarization Techniques: Revolutionizing Knowledge Understanding, IGI, 2014.
http://www.igi-global.com/chapter/newsum/96746
[2] G. Giannakopoulos, et al.: “Scaling and Semantically-Enriching Language-Agnostic Summarization” in Trends and Applications of Text Summarization Techniques (pp. 244-292). IGI Global, 2020.
[3] I. Dratsiou, et al.: “Assistive Technologies for Supporting the Wellbeing of Older Adults”, Technologies, 10(1), 8, 2022.
Please contact:
Paul Isaris, SciFY PNPC, Greece
George Giannakopoulos, SciFY PNPC, Greece










