by Ignacio M. Llorente and Rubén S. Montero (invited article)
OpenNebula is the result of many years of research and development in efficient and scalable management of virtual machines on large-scale distributed infrastructures. Its innovative features have been developed to address the requirements of business use cases from leading companies in the context of flagship European projects in cloud computing. OpenNebula is being used as an open platform for innovation in several international projects to research the challenges that arise in cloud management, and also as production-ready tool in both academia and industry to manage clouds.
As virtualization technologies mature at an incredibly rapid pace, there is a growing interest in applying them to the data-centre. After the success of cloud computing, companies are seeking reliable and efficient technologies to transform their rigid infrastructure into a flexible and agile provisioning platform. These so-called private clouds allow you to provide IT services with an elastic capacity, obtained from your local resources in the form of Virtual Machines (VM). Local resources can be further combined with public clouds in a hybrid cloud computing setup, thus enabling highly scalable hosting environments.
The main component involved in implementing this provision scheme is the Cloud Management Tool, which is responsible for the secure, efficient and scalable management of the cloud resources. A Cloud Management Tool provides IT staff with a uniform management layer across distributed hypervisors and cloud providers; giving infrastructure users the impression of interacting with a single infinite capacity and elastic cloud.
Because no two data centres are the same, building clouds is about integration and orchestration of the underlying infrastructure systems, services and processes. The Cloud Management Tool should seamlessly integrate any existing security, virtualization, storage, and network solutions deployed in the data-centre. Moreover, the right design and configuration in the Cloud architecture depend not only on the underlying infrastructure but also on the execution requirements of the service workload. The capacity requirements of the virtual machines as well as their level of coupling determine the best hardware configuration for the networking, computing and storage subsystems.
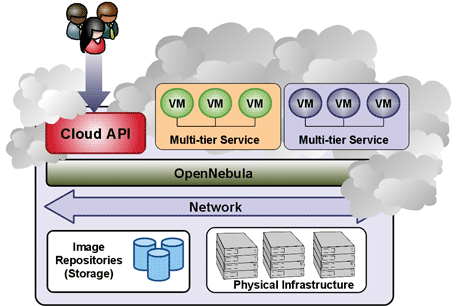
Figure 1: OpenNebula architecture.
OpenNebula is an open-source Cloud Management Tool that embraces this vision. Its open, architecture, interfaces and components provide the flexibility and extensibility that many enterprise IT shops need for internal cloud adoption. These features also facilitate its integration with any product and service in the cloud and virtualization ecosystem, and management tool in the data centre. OpenNebula provides an abstraction layer independent from underlying services for security, virtualization, networking and storage, avoiding vendor lock-in and enabling interoperability. OpenNebula is not only built on standards, but has also provided reference implementation of open community specifications, such us the OGF Open Cloud Computing Interface. This open and flexible approach for cloud management ensures widest possible market and user acceptability, and simplifies adaptation to different environments.
From Research Project to Open Software, Community and Ecosystem
OpenNebula was first established as a research project back in 2005 by the Distributed Systems Architecture Research Group at the Complutense University of Madrid. Since its first public release of software in March 2008, it has evolved through open-source releases to a strong user community and now operates as an open source project. The OpenNebula project has a strong commitment with open-source, being one of the few cloud management tools that are available under Apache license. The Apache license allows any cloud and virtualization player to innovate using the technology without the obligation to contribute those innovations back to the open source community.
The OpenNebula technology has matured thanks to an active and engaged community of users and developers. OpenNebula is downloaded several thousands times per month from its site, and the code can be also downloaded from the software repository and from several commercial and open-source distributions. The development is driven by its community in order to support the most demanded features, and by the international research projects funding OpenNebula in order to address the demanding requirements of several business and scientific use cases for cloud computing. OpenNebula has proved to be a production-ready solution that includes enterprise features such as security, robustness, scalability and performance that many IT shops need for internal cloud adoption, either in scientific or business environments.
Besides an exponential growth in its number of users, there are many projects, research groups and companies building new virtualization and cloud components to complement and to enhance its functionality. These components build the quickly evolving OpenNebula ecosystem, in which related tools, extensions and plug-ins are available from and for the community. Additionally, OpenNebula leverages the ecosystems being built around other popular cloud interfaces, such as Amazon AWS and VMware vCloud.
Outlook
OpenNebula is being funded by several Spanish projects, such as NUBA (strategic research program), BIOGRIDNET, Grid4Utility, HPCcloud and MEDIANET. Some of its main enhancements have been developed in RESERVOIR, flagship of European projects in cloud computing research. It is also used as core technology in many new European projects, such as StratusLab, aimed at bringing cloud and virtualization to grid computing infrastructures; BonFIRE, which targets the services research community on Future Internet, with the aim of designing, building and operating a multi-site cloud-based facility to support research across applications, services and systems; and 4CaaSt, aimed at creating an advanced PaaS Cloud platform which supports the optimized and elastic hosting of Internet-scale multi-tier applications.
Existing research funding ensures the engineering resources to support and develop OpenNebula and thus to maintain OpenNebula’s position as the leading and most advanced open-source technology to build cloud infrastructures. Additionally, C12G Labs is a new start-up that has been created to provide the professional integration, certification and technical support that many enterprise IT shops require for internal adoption. This also contributes to OpenNebula’s long term sustainability by ensuring that it is not tied exclusively to public financing.
Links:
DSA-Research: http://www.dsa-research.org
OCCI-WG: http://www.occi-wg.org
RESERVOIR: http://www.reservoir-fp7.eu
OpenNebula: http://www.opennebula.org
StratusLab: http://www.stratuslab.eu
BonFIRE: http://www.bonfire-project.com
4CaaSt: http://4caast.morfeo-project.org
C12G: http://www.c12g.com
Please contact:
Ignacio M. Llorente
Distributed Systems Architecture Research Group, Complutense University of Madrid, Spain
Tel: +34 91 3947616
E-mail:
Rubén S. Montero
Distributed Systems Architecture Research Group, Complutense University of Madrid, Spain
Tel: +34 91 3947538
E-mail:










