by Paolo Dario
Humans have moved beyond their evolutionary inheritance by progressively mastering nature through the use of tools and the development of culture. Current welfare, however, is not without challenges and its sustainability is at stake in our private, social, economic, urban and physical environments. One source of these challenges is the ageing of the population. In fact, in 40 years’ time nearly 35 per cent of the European population is projected to be 60 years old or over. Paradoxically the increase in life expectancy, is now creating new challenges. How to provide an ageing society with sustainable solutions in order to remain active, creative, productive, and above all, independent?
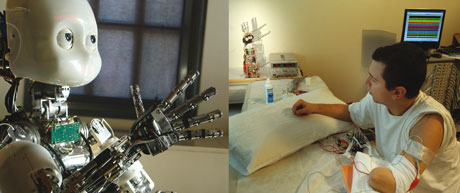
Figure: New sentient technology based on the natural principles underlying this phenomenon will be available to build the future generation of robots and prosthetics. iCub.org (photo © SPECS @ Universitat Pompeu Fabra) and CYBERHAND (photo © Università Campus Bio-Medico di Roma - Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna di Pisa).
We envisage that to achieve sustainable welfare will require a new class of machines and linked technologies, namely the Robot Companions for Citizens. These Robot Companions (RCs) will be a new generation of machines representing a true quantum leap compared to current robotic and mechatronic systems. RCs will be affordable, fully recyclable and a dependable technology for the foundation of a new sustainable welfare. RCs will be able to perform a multitude of assistive roles for humanity thanks to their capabilities to act and interact, physically, emotionally, socially and safely with humans. RCs will be ubiquitous yet unobtrusive, user-friendly and safe. This new generation of robots will extend the active independent lives of citizens, bolster the labour force, preserve and support human capabilities and experience. Also RCs will provide key services in our cities, aid us to cope with natural and man-made disasters and maintain our planet.
The drive to answer the grand scientific challenge of the RCC initiative requires, and will foster, an advanced understanding of the principles underlying the relationship between mind and body, the role of “matter” in building the mind, the natural design principles underlying brains and bodies, the relationship between structure and function and the principles that make living beings cognizant and sentient. In this context, sentience implies the need for the integration of feeling, emotion, perception, cognition and action.
The vision of RCC is that robotics becomes a platform for science and an active technology provider rather than a passive technology user: robotics as a method and technology to advance and validate natural principles of sentience and to translate them into synthetic ones. This paradigm shift will be based on the systematic and federated contribution and continuous involvement of several disciplines and communities that can be grouped as addressing: Matter, Body, Brain, Mind and Society. Matter includes nanotechnology, material science and tissue engineering supporting a new bodyware; biomaterials, and micro- and macro-scale cell biology, for developing bioartificial hybrid systems; nanofabrication technologies for energy storage, production and harvesting; Body: includes sensing, actuation and the construction of new compliant, light yet strong morphologies. Brain addresses neuroscience, in particular systems neuroscience for understanding the design principles of brains and the processes that allow their evolution, development, adaptation and maintenance in the real world; social neuroscience, cognition and sentience. Mind: includes the development and validation of the theoretical framework of sentience, communication, perception, cognition, emotion and action; the principles of human-human, human-robot and robot-robot interaction; principles of knowledge accumulation and expression. Society pertains to humanities and social sciences to favour the social integration and acceptability of the Robot Companions and facilitate their co-existence with humans, with attentive analysis to any potential ethical and legal implications. In this multidisciplinary and integrated framework RCC will develop experimental platforms of sentient robots at multiple scales of morphologies, complexity and sentience. These in turn will drive the delivery of specific human compatible deployment platforms.
Link: http://www.robotcompanions.eu
Please contact:
Paolo Dario
Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna, Italy
Coordinator of the CA-RoboCom Project
{jcomments on}









